Establishment & Operation
of Hydrogen Valley
Innovation Cluster in Odisha
Empowering Odisha's Green Future, Innovating Hydrogen Solutions for Tomorrow

Establishment & Operation of Hydrogen Valley Innovation Cluster in Odisha
Empowering Odisha's Green Future, Innovating Hydrogen Solutions for Tomorrow
About
The Odisha Hydrogen Valley Innovation Cluster aims to spearhead developing and managing cutting-edge hydrogen technologies, with IIT Bhubaneswar at the helm. This initiative aligns with India’s commitment to achieve 500 GW of non-fossil fuel power capacity by 2030, as announced by the Honourable Prime Minister at COP26. The project seeks to advance hydrogen production, storage, and transportation technologies through a collaborative approach, integrating local and national research institutions, industry leaders, and government bodies. Odisha’s strategic advantages, including its mineral wealth, solar resources, and supportive hydrogen energy policy, position it as a prime location for this innovative endeavor.
The cluster’s development will unfold in three phases: short-term (1-2 years), medium-term (1-5 years), and long-term (1-7 years). Initially, it will focus on establishing small-scale green hydrogen operations and refining existing technologies with partners. The medium term will scale these technologies for broader applications, including mining and steel production, while the long term will target the decarbonization of hard-to-abate industries. This initiative promises significant economic benefits and positions India as a global leader in green industrialization while fostering job creation and addressing climate change challenges.
Mission
The National Green Hydrogen Mission is designed to be implemented in two distinct phases, driving the growth and adoption of green hydrogen technologies in India.
Phase 1 (2022-23 to 2025-26) focuses on laying the groundwork for the green hydrogen sector. This includes driving demand creation, advancing research and development, and scaling up domestic electrolyzer manufacturing. Key pilot projects will be initiated to promote green transitions in steel production, heavy-duty mobility, and shipping. Additionally, efforts will begin to establish a regulatory and standards framework to support sector growth and align with international norms.
Phase 2 (2026-27 to 2029-30) will build on the successes and cost reductions achieved in Phase 1. This phase aims to explore commercial-scale green hydrogen projects across steel, mobility, and shipping sectors, and pilot projects in other sectors such as railways and aviation. R&D activities will be scaled up to continuously improve products, enhancing green hydrogen’s penetration across all potential sectors and driving deep decarbonization of the economy.
Project Stakeholders
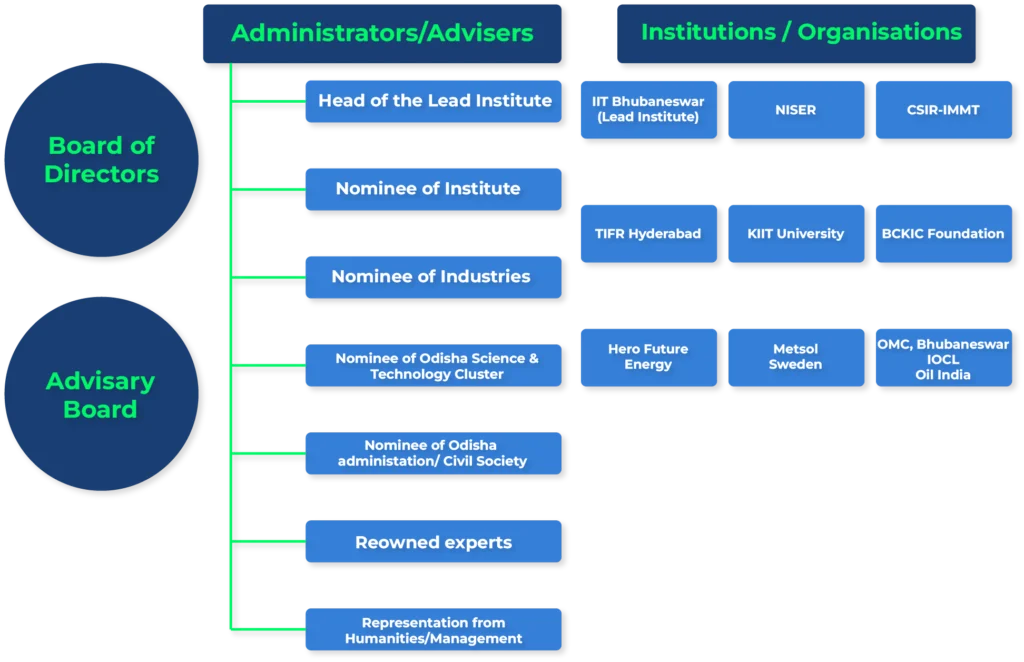
Green Hydrogen Project Stakeholders and Responsibilities

Indian Institute of Technology Bhubaneswar
IIT Bhubaneswar provides an excellent academic environment and cutting-edge research opportunities. The institution focuses on promoting globally competitive academic programs, expanding interdisciplinary research, and improving the quality of life through technology. IIT BBS will contribute to R&D support for technological advancements, including exploring hydrogen generation technologies like photoelectrochemical and biohydrogen.

CSIR-Institute of Minerals and Materials Technology

National Institute of Science Education and Research
Bhubaneswar City Knowledge Innovation Cluster Foundation

Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Hyderabad

Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology Bhubaneswar

Metsol, Sweden

Hero Future Energies

Odisha Mining Corporation Limited

Dalmia Cement (Bharat) Ltd

Jindal Steel and Power Limited
Objectives of the Consortium
❖ Strengthen the knowledge and skills of stakeholders along the hydrogen value chain.
❖ Demonstrate clean hydrogen solutions for local, regional, and nationwide deployment, addressing production, distribution, storage, and use.
❖ Increase public and private awareness, acceptance, and uptake of clean hydrogen technologies.
❖ Develop and commercialize new hydrogen products and processes.
❖ Improve existing products, processes, and applications with reduced material and energy consumption, cost reductions, and enhanced competitiveness.
❖ Develop technologies or designs that meet or exceed occupational health and safety standards.
Expected project outcomes
❖Focus on indigenous technology development in both production and application areas while leveraging the geographical advantages of Odisha state
❖ Selection in line with greening of hard to abate sectors having significant economic potential.
❖ Innovations for greening the steel sector Maintaining lead as the world’s second-largest steel producer while being carbon competitive in evolving norms.
❖ Keeping mining sectors competitive by retrofitting existing trucks leading to limited financial exposure for their gree ning efforts Retrofitted trucks also provide greening opportunities to coal mines.
❖Supporting JUST transition in Odisha in long term while transitioning from coal to green energy.

